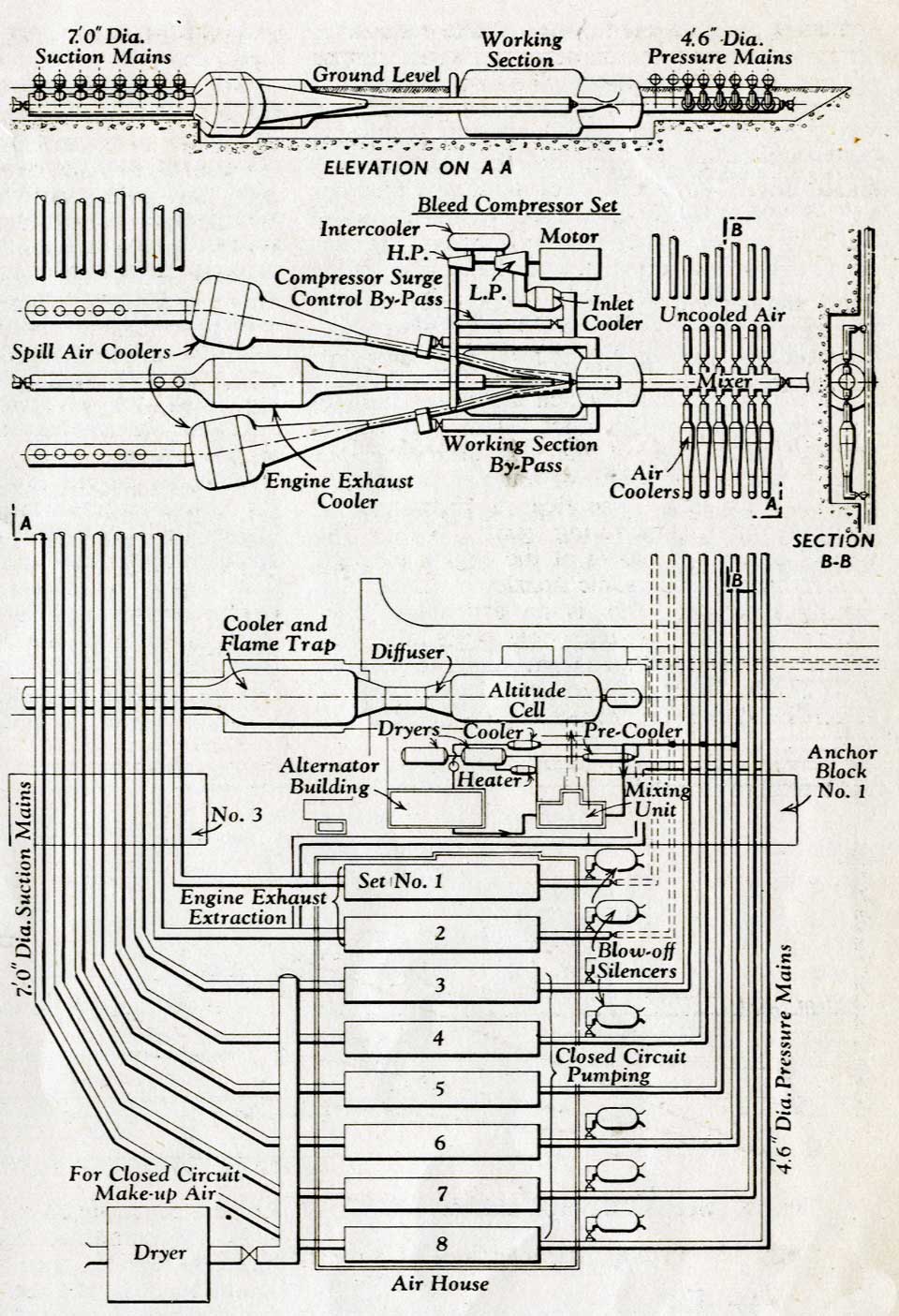
“When consideration of air services and test arrangements began, it was quite impossible to say what
the final air demands would prove to be. Considerable research was needed to establish supersonic
test techniques and their efficiency. For the same reasons, the groupings of different tests within
one installation could not be predicted accurately, that is, the air distribution needs were not
defined. It was therefore necessary to adopt a scheme flexible in air compression and evacuation
duty and a flexible air distribution scheme. The air pumping plant consists of eight sets of three
machines which can run as compressors or exhausters in 3 to 1 or 9 to 1 staging. Each set has
individual pressure and exhaust mains all going to the main test site. A cross-over main feeds the
output of seven sets into the eighth set which permits site evacuation of 1/27 or
1/81 of an
atmosphere. Variable degrees of inter-cooling and after-cooling can be used to vary the delivery
temperature and to a lesser degree, the pressure ratio of the sets. This arrangement has proved to
be very adaptable indeed. arrangements of blow and suck varying in quantity and degree can be chosen
freely at any place for any purpose without compromising other needs at different times and places,
and it has proved possible to plan subsequently with convenience all tests and emplacements as their
duty is fully defined.”